Describe the Stages of Cellular Respiration
Cellular respiration is a collection of three unique metabolic pathways. How each process is linked to specific organelles within the eukaryotic.

3 Stages Of Cellular Respiration Cellular Respiration Teaching Biology Writing Words
The raw materials products and amount of ATP or glucose produced during each phase.

. Oxygen is an important part of. Ensure you include 1 the three stages 2 what is produced at each stage and 3 the amount of ATP produced at each of the three stages. Inner membrane and inner membrane space of mitochondria.
In glycolysis glucosea six-carbon sugarundergoes a series of chemical transformations. 4 Stages of Cellular Respiration. Stage 3 of cellular respiration.
Briefly describe the process of cellular respiration. Splitting sugars in cytoplasm energy investment phase - 2 ATP molecules combine with glucose molecule. A Glycolysis b Krebs Cycle c Electron Transport Chain.
A small amount of energy is also released. Completes breakdown of carbon dioxide makes small amounts of ATP provides electrons. The bridge reaction which stets the stage for aerobic respiration.
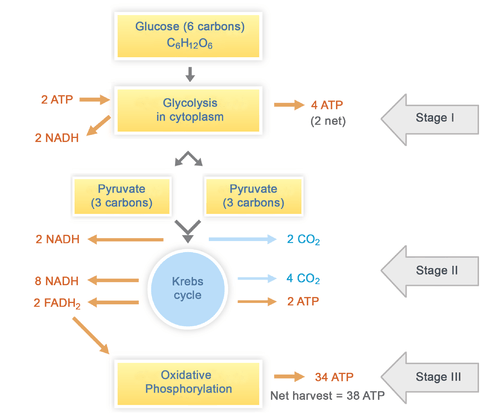
Glycolysis breaks down glucose into 2 Pyretic Acid Molecules in the Cytoplasm releasing 2 ATP and Hydrogen. And the Krebs cycle and the electron transport chain oxygen-dependent pathways that occur in sequence in the mitochondria. Glycolysis pathway EmbdenMeyerhof pathway The transition reaction oxidative decarboxylation Krebs cycle citric acid cycle Oxidative phosphorylation in mitochondria Glycolysis pathway EmbdenMeyerhof pathway Glycolysis - breaking sugar.
Pyruvates moving into mitochondria through oxidation pyruvates broken into water. The cellular respiration process includes four basic stages or steps. Account for all electron carriers and ATP molecules produced.
The first step of cellar respiration called glycolysis takes place in the cytoplasm. The stage happens in cytoplasm. The ETC takes place in the inner mitochondrial membrane.
Glycolysis is an anaerobic process while the other two pathways are aerobic. The ETC makes 34 ATP 30 from 10 NADH 4 from FADH2 returns the electron acceptor molecules 10 NAD and 2 FAD so that they can be used again in cellular respiration and combines the H ions. Steps of cellular respiration.
The three stages of cellular respiration include glycolysis electron transport chain and citric acid cycle also known as Krebs cycle or tricarboxylic acid cycle. The stage happens in mitochondria. The first of these stages is called glycolysis.
This molecule stores the energy released during respiration and allows the cell to transfer this energy to various parts of the cell. Some of the importance stages of aerobic respiration are as follows. Each pyruvate from glycolysis goes into the mitochondrial matrixthe innermost compartment of.
6 pts Briefly describe the processes involved for maintaining our body temperature. Clearly explain the importance of OXYGEN in. Carbs Proteins and Fats.
Glucose is broken down. Cellular respiration steps 4 distinct steps of cellular respiration include. Cellular respiration and photosynthesis form a critical cycle of energy and matter that supports the continued existence of life on earth.
Glycolysis Link reaction Krebs cycle and Electron transport chain. While the process can seem complex this page takes you through the key elements of each part of cellular respiration. For example an enzyme may need energy from ATP to.
This is where the small molecules combine with oxygen to produce water carbon dioxide and a large amount of energy. Oxygen combines with small molecules. Stage 2 of cellular respiration.
Glycolysis the citric acid cycle and the electron transport chain. Respiration consists of a complicated series of chemical reactions. In the end it gets converted into two molecules.
Describe the role of oxygen in cellular respiration Cellular respiration is the process that produces energy in cells. The first stage of cellular respiration occurs in the cytoplasm. Be able to do energy accounting for each stage of cellular respiration.
Compare and contrast the 3 stages of cellular respiration. All About Cellular Respiration. Anatomy and Physiology questions and answers.
Glycolysis literally means splitting sugars and it is the 10-step process by which sugars are released for energy. Glycolysis which occurs in all organisms prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Be sure to include the following in your submission.
The second stage occurs in the mitochondria. Name and describe the purpose of the 2 electron carriers that participate in cellular respiration. The two main components are oxygen andshow more content The last step of cellular respiration is the Electron transport chain ETC.
ATP is used by a number of cellular components as a source of energy. Aboard the Electron Transport Train. Which statements best describe the first stage of cellular respiration.
The main product of any cellular respiration is the molecule adenosine triphosphate ATP. The Krebs Cycle takes Citric Acid which is a derivative of Pyruvic Acid and converts this through 4 cycles into Hydrogen. The metabolism of glucose and energy production occurs in four stages.
2 pts Question. In a 1-2 page Word document describe the stages of cellular respiration and photosynthesis and their interaction and interdependence. Cellular respiration when takes place in the presence of oxygen it is known as aerobic and in the absence of oxygen is known as anaerobic respiration or fermentation.
Aerobic Respiration is the process by which the energy from glucose is released in the presence of oxygen. Cassandra made a Venn diagram to compare and contrast the two stages of cellular respiration. The three main stages of cellular respiration aerobic would include Glycolysis the Krebs Cycle and the Electron Transport Chain.
Cellular respiration is a three stage process your body undergoes to produce ATP. This is where glucose is broken down into smaller molecules. Describe the stages of cellular respiration and photosynthesis and their interaction and interdependence including raw materials products and amount of ATP or glucose produced during each phase.

Cellular Respiration Ck 12 Foundation

Comments
Post a Comment